Benedict modified the Fehling solution to produce a fairly stable, enhanced single reagent. As a chelating agent, Sodium Citrate works. It is very sensitive and sufficient precipitates are produced by even small amounts of sugar reduction (0.1 percent).
Reaction
Reagents:
Qualitative reaction of Benedict:
Dissolve 173g of Sodium Citrate and 100g of Anhydrous Sod. In about 800mL of water, carbonate by gently heating the contents. Then, dissolve 17.3g of copper sulfate in about 100mL DW in a separate beaker. Slowly pour this solution into the Carbonate-Citrate mixture with constant stirring, and make up to 1 L with DW.
Procedure:
- To add about 2 mL of Benedict's reagent, add 0.5-1 mL of the test solution.
- Keep the test tubes in a bath of boiling water.
- Note that green, orange, yellow or red precipitates are formed, indicating the presence of sugar reduction in the solution.
Note:
- This test is particularly suitable for urinary sugar reduction detection because it is more specific than the Fehling test, which is also positive for non-reducing substances such as urates present in urine.
- This is a semi-quantitative test.
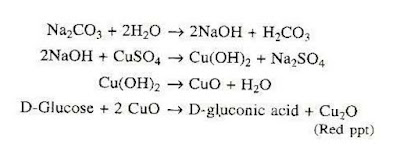
0 komentar
Posting Komentar