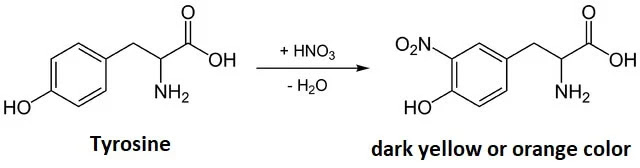
The xanthoproteic test is a chemical test that is used to identify the presence of certain amino acids in a sample. The test involves the use of concentrated nitric acid, which reacts with specific amino acids to produce a yellow color. This test is particularly useful for identifying the amino acids tyrosine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan, which are all aromatic amino acids.
Principle
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and there are 20 different types of amino acids that make up the proteins in our bodies. Each amino acid has a unique chemical structure, and they can be classified into different categories based on their properties. Aromatic amino acids are those that contain a ring structure in their chemical makeup, which gives them unique properties.
 |
| Principle of xanthoproteic test |
The xanthoproteic test is a simple and reliable test that can be used to identify the presence of these aromatic amino acids. The test involves adding a small amount of concentrated nitric acid to a sample of the substance being tested. If the sample contains tyrosine, phenylalanine, or tryptophan, the nitric acid will react with these amino acids to produce a yellow color. The intensity of the color can be used to determine the concentration of the amino acid in the sample.
Procedure
- To 2 mL amino acid solution in a test tube, add equal volume of concentrated HNO3, white precipitate is formed.
- Heat over a flame for 1 min and observe that some precipitate is redissolves.
- Now cool thoroughly under the tap water.
- Add 2 ml of 40% NaOH and mix.
- Observe the color.
Positive result
The xanthoproteic test is a useful tool for identifying the presence of these amino acids in a variety of substances. It can be used to test for the presence of tyrosine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan in foods, supplements, and other substances. The test is relatively simple to perform and requires only a small amount of the sample being tested.
- Tyrosine is an amino acid that is produced in the body from phenylalanine. It is found in many proteins, including those that are involved in transmitting signals in the nervous system. Tyrosine is also a precursor for the production of several important neurotransmitters, including dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.
- Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained from the diet. It is found in many foods, including meats, dairy products, and soybeans. Phenylalanine is used by the body to produce several important molecules, including tyrosine, dopamine, and norepinephrine.
- Tryptophan is another essential amino acid that is found in many foods, including meats, dairy products, and grains. It is used by the body to produce several important molecules, including serotonin and melatonin. Tryptophan is also used by the body to synthesize niacin, which is an important B vitamin.
 |
| Result of xanthoproteic test |
To perform the xanthoproteic test, a small amount of the sample being tested is placed in a test tube or other container. A few drops of concentrated nitric acid are then added to the sample, and the mixture is observed for the appearance of a yellow color. If a yellow color develops, it indicates the presence of one or more of the aromatic amino acids.
The intensity of the yellow color can be used to estimate the concentration of the amino acid in the sample. If the concentration is very low, the color may be very faint or barely visible. If the concentration is high, the color may be very intense and deep yellow in color.
The xanthoproteic test is just one of many different chemical tests that can be used to identify the presence of amino acids and other molecules in a sample. Other tests include the biuret test, the ninhydrin test, and the Sakaguchi test. Each of these tests uses different chemical reagents to identify specific molecules in a sample.
In conclusion, the xanthoproteic test is a simple and reliable test that can be used to identify
0 komentar
Posting Komentar